Optics formulas
Remember that: \( \vec{a} = \mathbf{a} \), \(\dot{a}= \frac{da}{dt}\)
and \(\Delta a = a_{final} - a_{initial} = a_{f} - a_{i} = a_{2} -
a_{1} \). The \(\propto\) symbol is read as "is proportional to".
While \(\hat{a} = \frac{\vec{a}}{\Vert \vec{a} \Vert}\) is the unit
vector.
Symbols
name
symbol
amplitude
$$A$$
slit width
$$a$$
light velocity
$$c = 299\ 792\ 458\ \mathrm{m/s}$$
distance
$$d$$
energy
$$E$$
focal length, frequency
$$f$$
Planck constant
$$\begin{split} h &= 6.626 \times 10^{-34}\ \mathrm{J \cdot s}
\\ &= 4.136 \times 10^{-15}\ \mathrm{eV \cdot s} \end{split}$$
intensity
$$I$$
distance from diffraction slits to screen
$$L$$
angular magnification (or amplification)
$$M$$
lateral magnification, diffraction number of order
$$m$$
near point approximation
$$NP$$
refractive index
$$n$$
optical power
$$P$$
curvature radius (spherical mirror)
$$r$$
object distance
$$s$$
image distance
$$s^{\prime}$$
speed of light in a medium
$$v$$
object height
$$y$$
image height
$$y^{\prime}$$
phase difference
$$\delta$$
wavelength
$$\lambda$$
subtended angle
$$\theta$$
phase difference of several waves
$$\phi$$
Geometrical optics
name
equation
refractive index
$$n = \frac{c}{v}$$
reflection law
$$\theta_{i} = \theta_{r}$$
Snell's law of refraction
$$n_{1} \sin \theta_{1} = n_{2} \sin \theta_{2}$$ $$\frac{\sin
\theta_{1}}{v_{1}} = \frac{\sin \theta_{2}}{v_{2}}$$
reflected intensity
$$I = \left( \frac{n_{1} - n_{2}}{n_{1} + n_{2}} \right)^{2}
I_{0}$$
total internal reflection critical angle
$$\sin \theta_{c} = \frac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}$$
Malus law
$$I = I_{0} \cos^{2} \theta$$
Brewster angle, polarization angle
$$\tg \theta_{p} = \frac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}$$
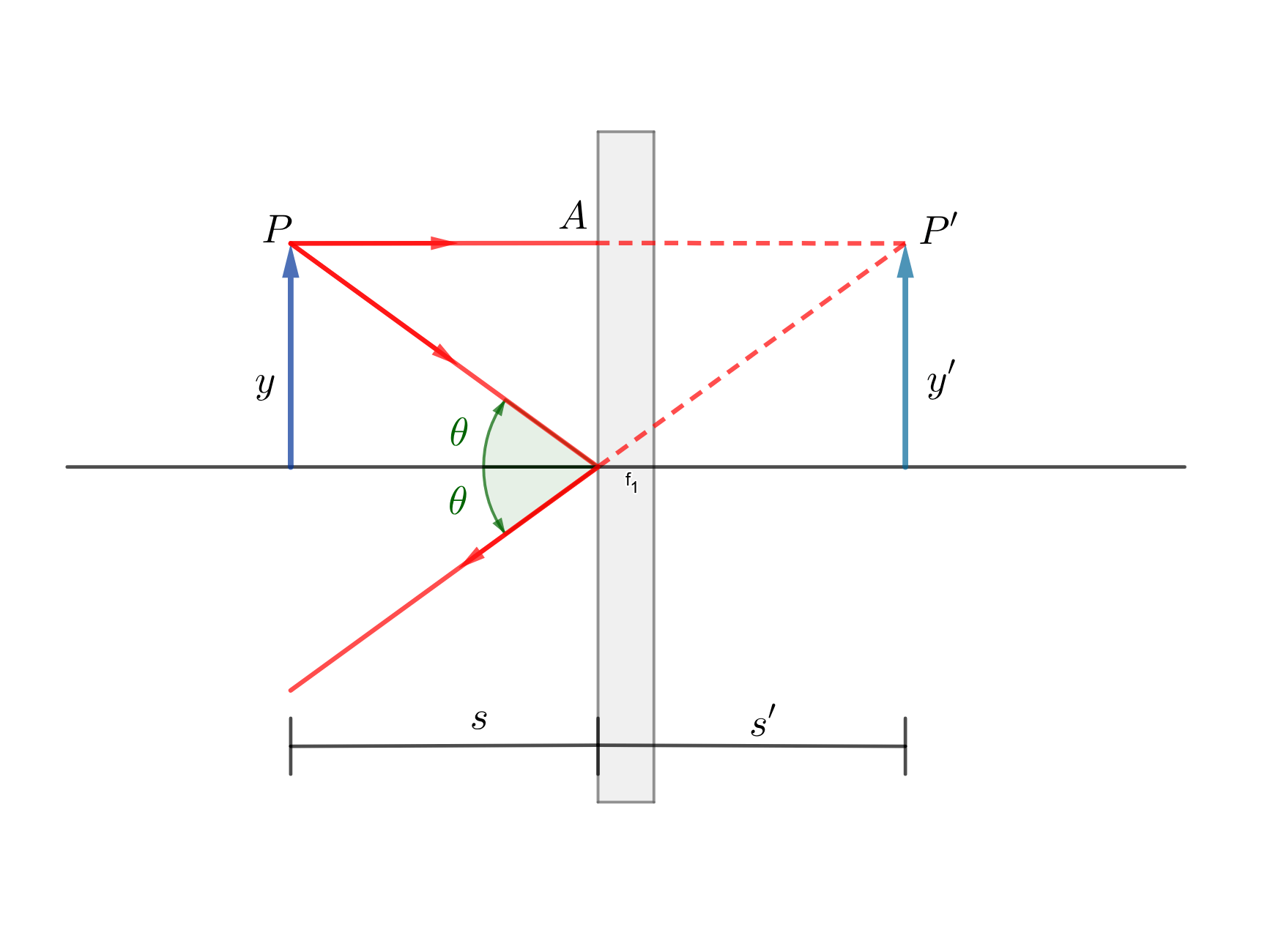
Flat mirror.
Spherical mirror
name
equation
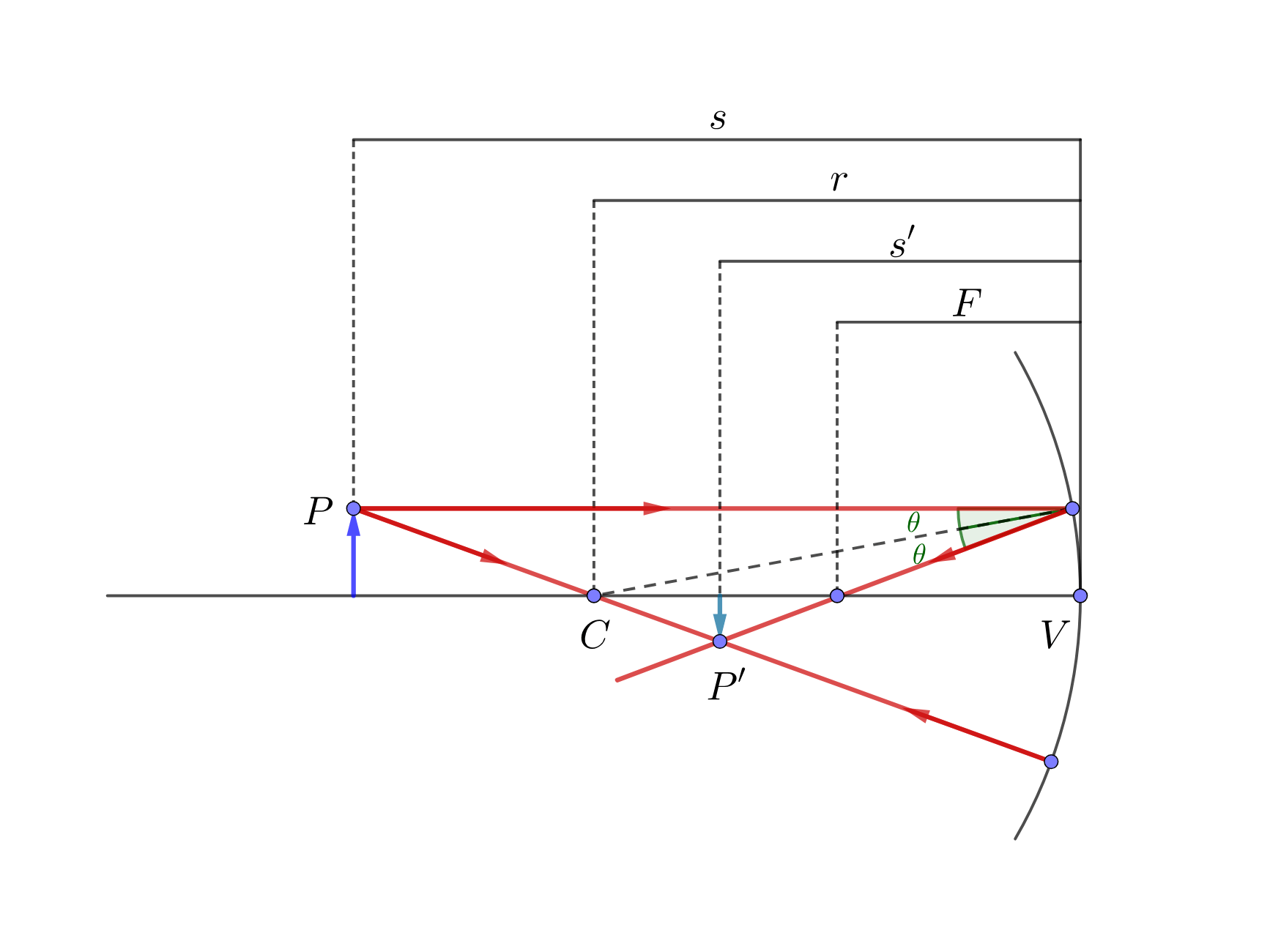
mirror equation
$$\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{s} + \frac{1}{s^{\prime}}$$
focal length of a mirror
$$f = \frac{1}{2}r$$
lateral magnification
$$m = \frac{y^{\prime}}{y} = - \frac{s^{\prime}}{s}$$
lateral magnification using curvature radius
$$\frac{y^{\prime}}{y} = - \frac{r/2}{s - \left( r/2 \right)}$$
Spherical mirror.
Lenses
name
equation
refraction on a single surface
$$\frac{n_{1}}{s} + \frac{n_{2}}{s^{\prime}} = \frac{n_{2} -
n_{1}}{r}$$
magnification due to a refracting surface
$$m = \frac{y^{\prime}}{y} = - \frac{n_{1} s^{\prime}}{n_{2}s}$$
lens maker equation
$$\frac{1}{f} = \left( n - 1 \right) \left( \frac{1}{r_{1}} -
\frac{1}{r_{2}} \right)$$
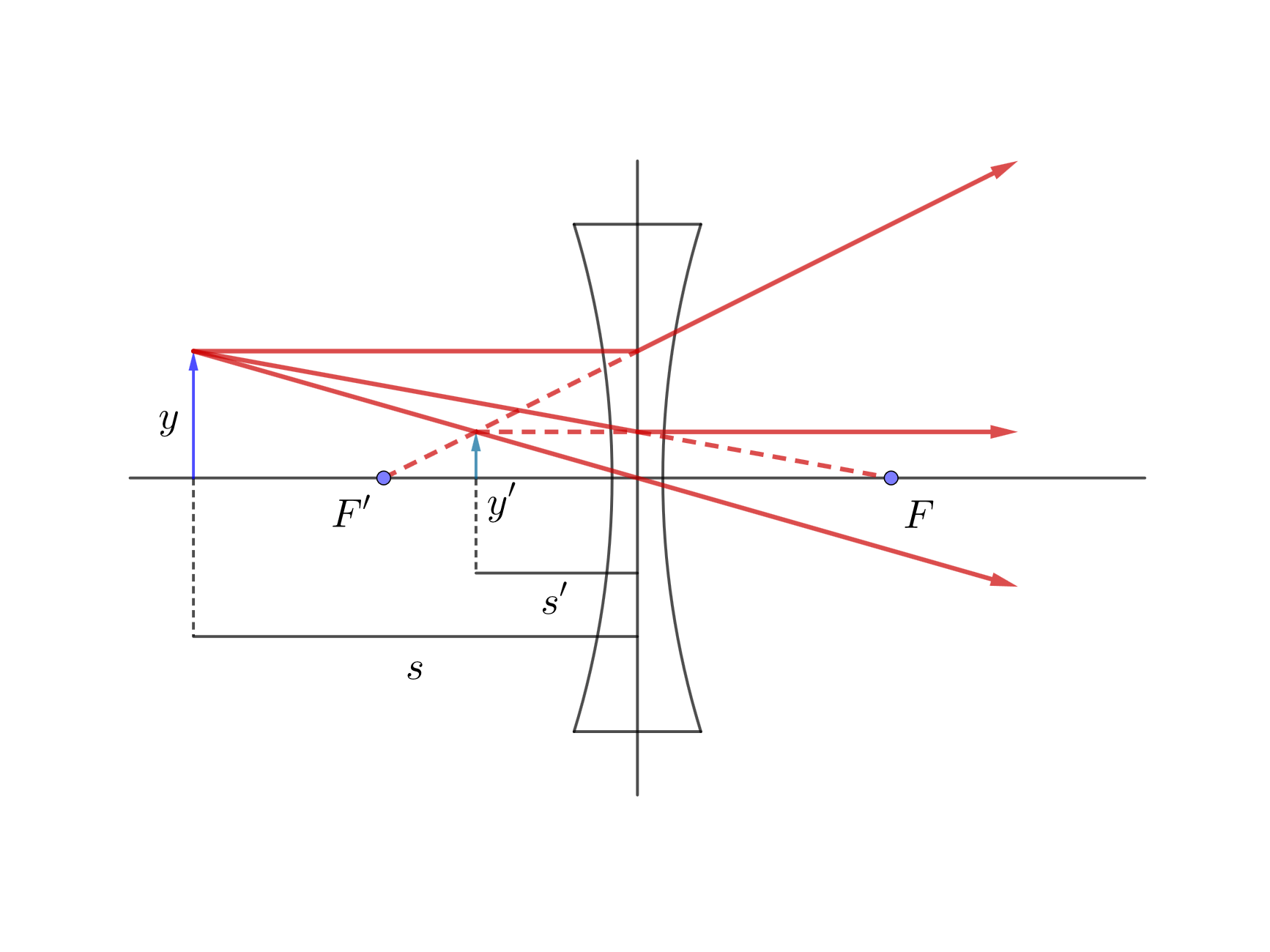
thin lens equation
$$\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{s} + \frac{1}{s^{\prime}}$$
optical power
$$P = \frac{1}{f}$$
effective focal length of two lenses
$$\frac{1}{f_{ef}} = \frac{1}{f_{1}} + \frac{1}{f_{2}}$$
optical power of two lenses
$$P_{ef} = P_{1} + P_{2}$$
subtended angle for the eye
$$\theta = \frac{y}{s}$$
subtended angle for near point
$$\theta = \frac{y}{NP}$$
subtended angle with lens
$$\theta = \frac{y}{f}$$
lens angular magnification (or amplification)
$$M = \frac{\theta}{\theta_{o}} = \frac{NP}{f}$$
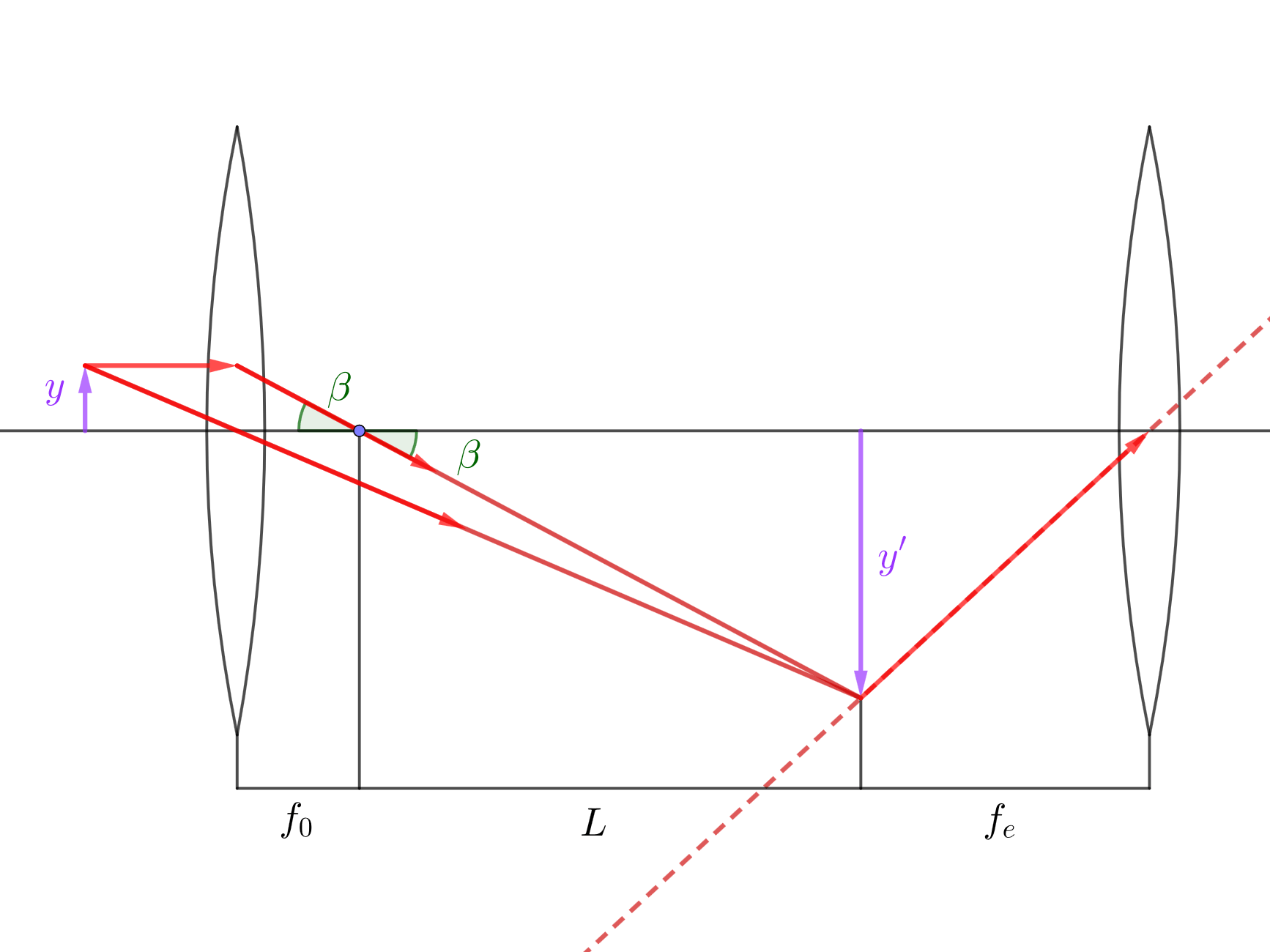
microscope objective lens lateral magnification
$$m_{o} = \frac{y^{\prime}}{y} = - \frac{L}{f_{o}}$$
ocular lens angular magnification
$$M_{e} = \frac{x_{pp}}{f_{e}}$$
microscope angular magnification
$$M = m_{o}M_{e} = - \frac{L}{f_{o}}\frac{x_{pp}}{f_{e}}$$
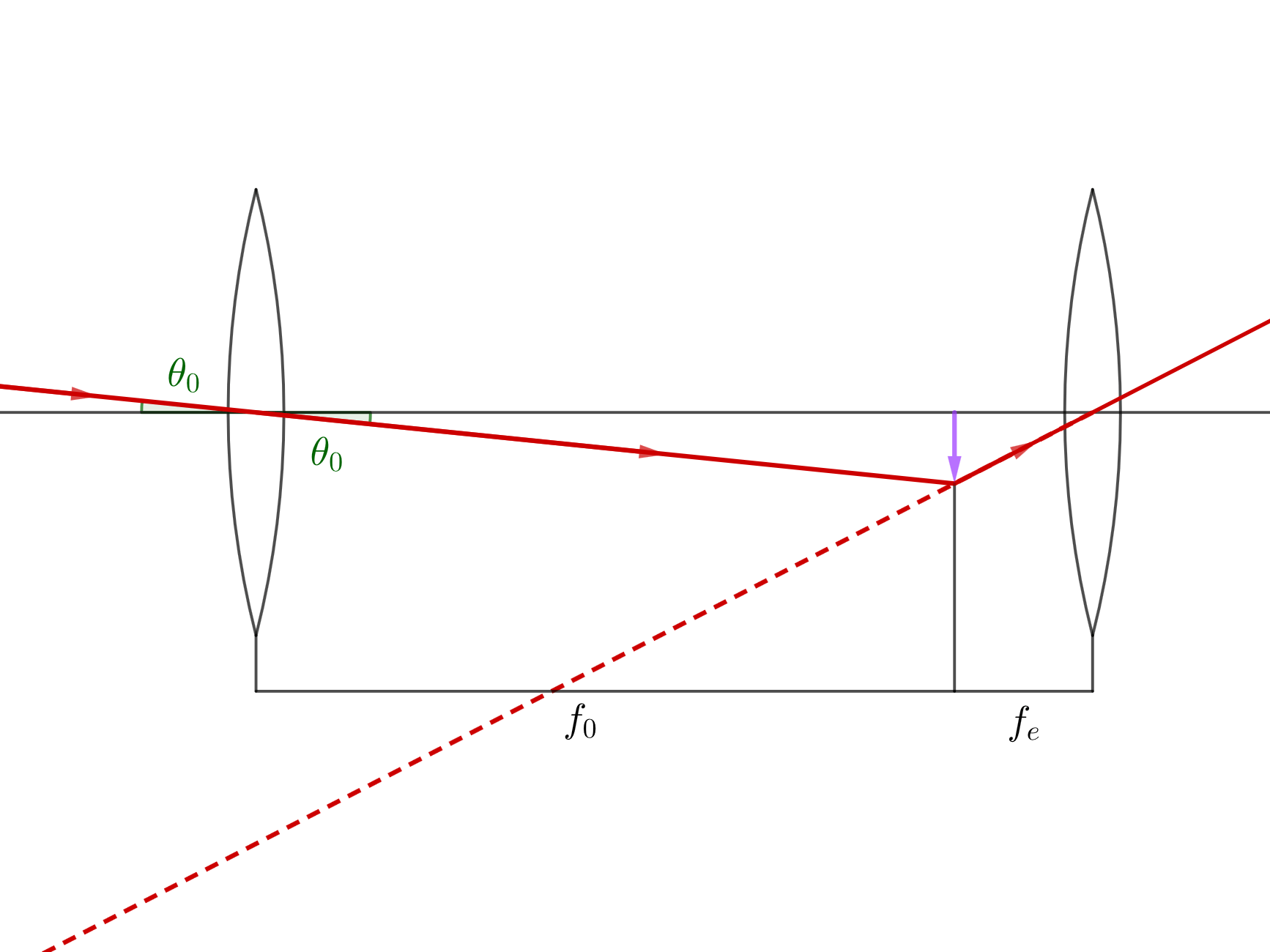
telescope angular magnification
$$M = \frac{\theta_{e}}{\theta_{o}} = - \frac{f_{o}}{f_{e}}$$
Convex Lens.
Concave Lens.
Microscope diagram.
Telescope diagram.
Physical optics
Two slit interference
name
equation
phase difference due to the difference in the optical path
traveled
$$\delta = \frac{\Delta r}{\lambda} 2\pi = \frac{\Delta
r}{\lambda} 360\ ^{\circ}\mathrm{C}$$
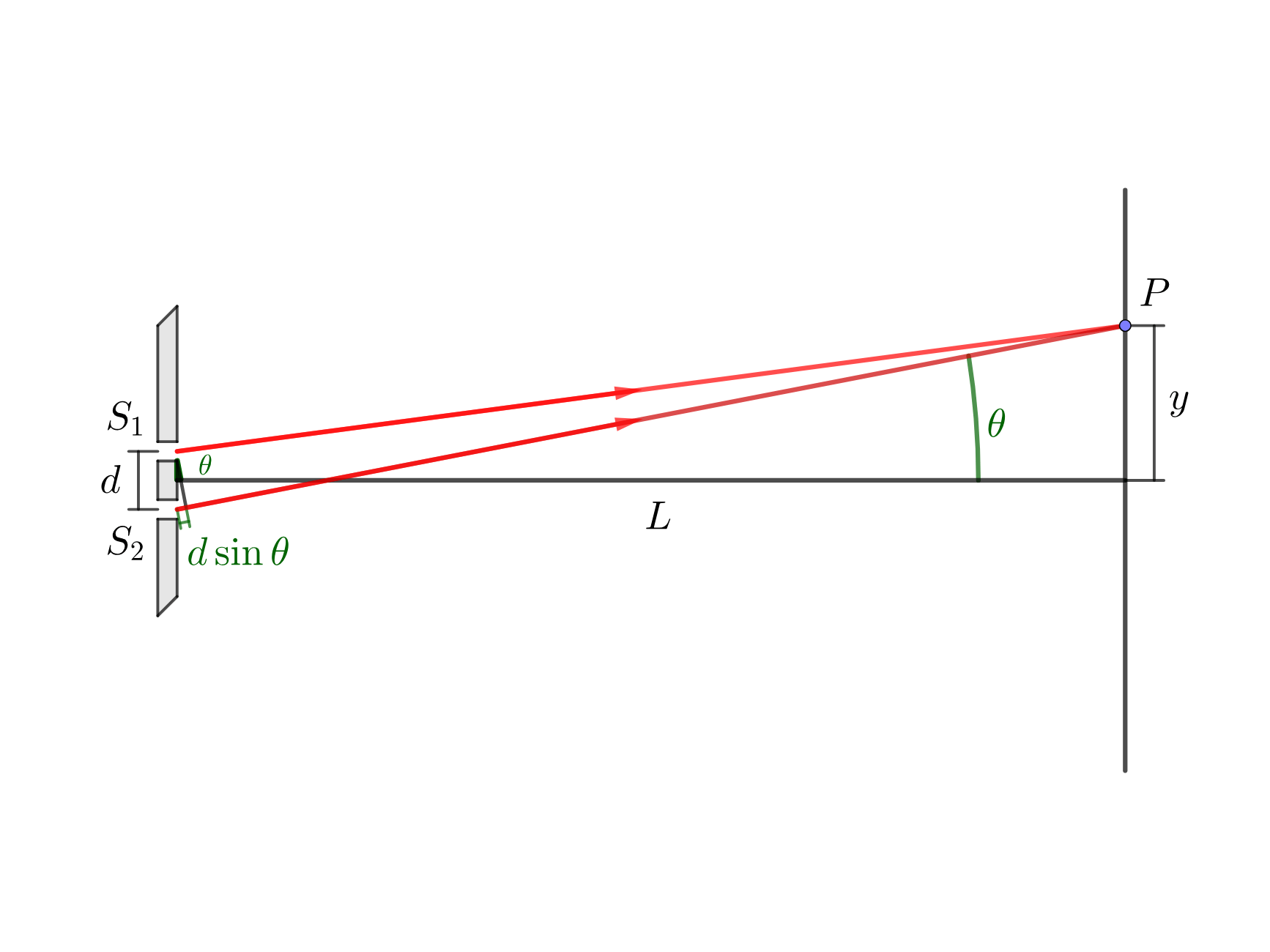
two-slit interference maxima
$$d \sin \theta_{\max} = m\lambda,\quad m = 0,1,2, \ldots$$
two-slit interference minima
$$d \sin \theta_{\min} = \left( m - \frac{1}{2}
\right)\lambda,\quad m = 1,2,3, \ldots$$
two-slit phase difference
$$\frac{\delta}{2 \pi}= \frac{d \sin \theta}{\lambda}$$
distance on the screen to the m-th bright fringe
$$y_{m} = m \frac{\lambda L}{d}$$
intensity as a function of phase difference
$$I = 4 I_{0} \cos^{2} \frac{1}{2} \delta$$
Two slit diagram.
One slit diffraction
name
equation
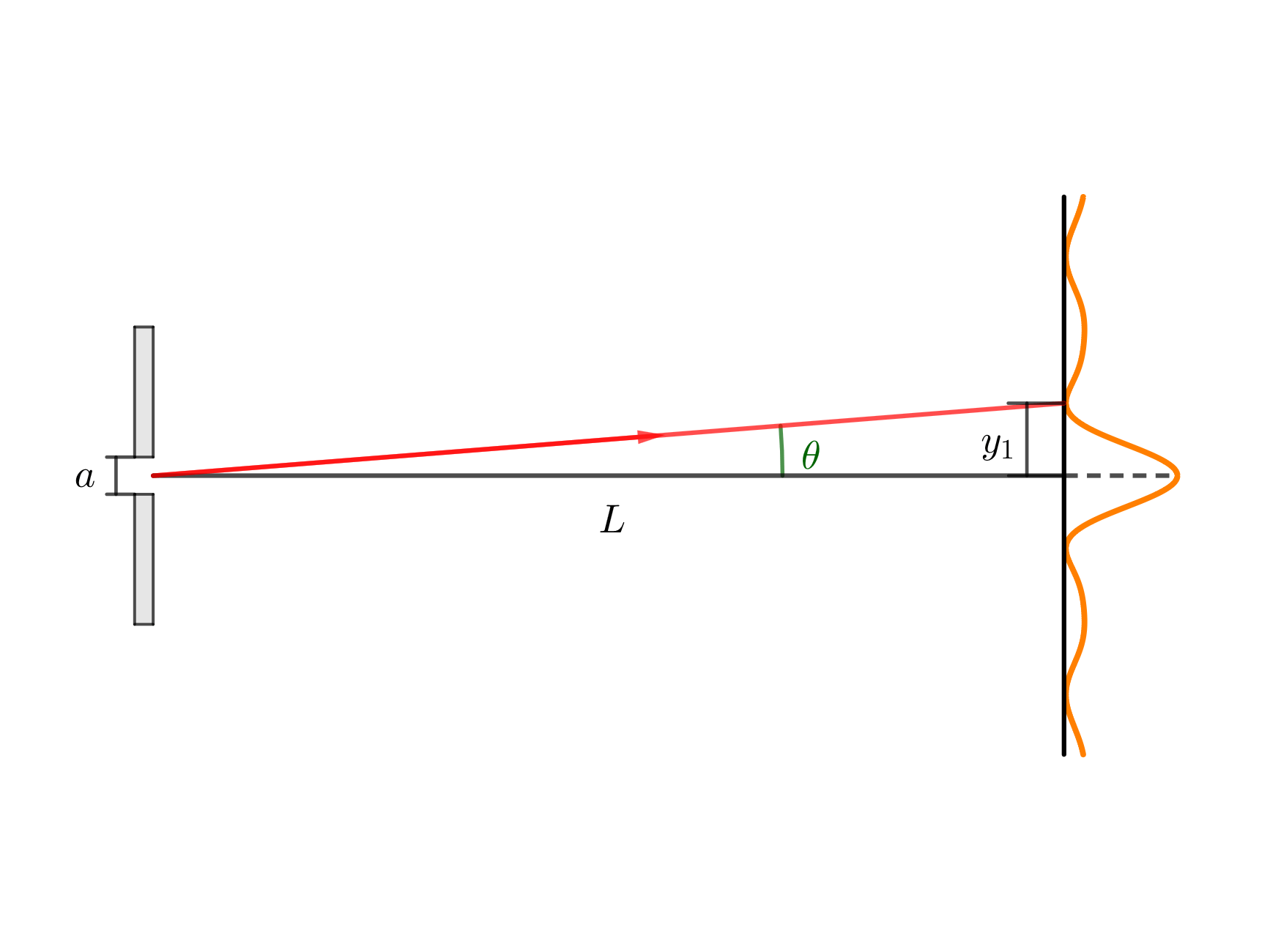
intensity null values
$$a\sin \theta = m \lambda, \qquad m = 1,2,3, \ldots$$
zero intensity minima
$$\tg \theta_{1} = \frac{y_{1}}{L}$$
diffraction intensity of a slit
$$I = I_{0} \left( \frac{\sin \frac{1}{2} \phi}{\frac{1}{2}
\phi} \right)^{2}$$
Single slit diagram.
Quantum optics
name
equation
equation for photon energy
$$E = hf = \frac{hc}{\lambda}$$
hc product
$$hc = 1240\ \mathrm{eV \cdot nm}$$
photon energy
$$\vert \Delta E \vert = hf$$
emitted wavelength
$$\lambda = \frac{c}{f} = \frac{hc}{\vert \Delta E \vert}$$